Summary of Technologies and Diagnostic Equipment
Below you will information relating to the different technology and diagnostic terms you may hear during your appointment or treatment.
 Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a noninvasive imaging technology used to obtain high resolution cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT is similar to ultrasound testing, except that imaging is performed by measuring light rather than sound. The OCT measures the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and the results are used for managing glaucoma, macular degeneration and other ocular diseases.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a noninvasive imaging technology used to obtain high resolution cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT is similar to ultrasound testing, except that imaging is performed by measuring light rather than sound. The OCT measures the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and the results are used for managing glaucoma, macular degeneration and other ocular diseases.
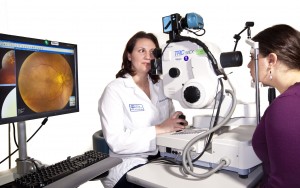 Fundus photography documents the retina and optic nerve tissues in the eyes which translates the optical images we see into the electrical impulses our brain understands. The retina can be photographed directly as the pupil is used as both an entrance and exit for the fundus camera’s illuminating and imaging light rays. An ophthalmic photographer focuses and aligns the fundus camera. Ophthalmologists use these retinal photographs diagnose, follow, and treat eye diseases. The images are also used to show you the status of your eye. Fundus photos are a tool that the doctor can use to discuss any findings as you determine future care.
Fundus photography documents the retina and optic nerve tissues in the eyes which translates the optical images we see into the electrical impulses our brain understands. The retina can be photographed directly as the pupil is used as both an entrance and exit for the fundus camera’s illuminating and imaging light rays. An ophthalmic photographer focuses and aligns the fundus camera. Ophthalmologists use these retinal photographs diagnose, follow, and treat eye diseases. The images are also used to show you the status of your eye. Fundus photos are a tool that the doctor can use to discuss any findings as you determine future care.
 The visual field test is a subjective measure of central and peripheral vision, or “side vision,” and is used by your Ophthalmologist to diagnose, determine the severity of, and monitor glaucoma. A visual field test is performed as soon as glaucoma is suspected. Visual field tests assess the potential presence of blind spots (scotomas). A blind spot in the field of vision can be linked to a variety of specific eye diseases, depending on the size and shape of the scotoma. The most common visual field test uses a light spot that is repeatedly presented in different areas of your peripheral vision. It evaluates vision loss due to glaucoma, damage to the visual pathways of the brain, and other optic nerve diseases. When glaucoma is diagnosed the visual field data is used to determine the severity of disease. This staging information is useful in choosing a target intraocular pressure and determining follow-up.
The visual field test is a subjective measure of central and peripheral vision, or “side vision,” and is used by your Ophthalmologist to diagnose, determine the severity of, and monitor glaucoma. A visual field test is performed as soon as glaucoma is suspected. Visual field tests assess the potential presence of blind spots (scotomas). A blind spot in the field of vision can be linked to a variety of specific eye diseases, depending on the size and shape of the scotoma. The most common visual field test uses a light spot that is repeatedly presented in different areas of your peripheral vision. It evaluates vision loss due to glaucoma, damage to the visual pathways of the brain, and other optic nerve diseases. When glaucoma is diagnosed the visual field data is used to determine the severity of disease. This staging information is useful in choosing a target intraocular pressure and determining follow-up.
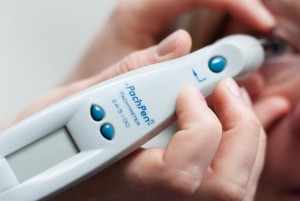 Pachymetry is a simple, painless test to measure the thickness of your cornea — the clear window at the front of the eye. A probe called a pachymeter is gently placed on the front of the eye (the cornea) to measure its thickness. Pachymetry can help your diagnosis, because corneal thickness has the potential to influence eye pressure readings. With this measurement your Ophthamologist can better understand your eye pressures readings and develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Pachymetry is a simple, painless test to measure the thickness of your cornea — the clear window at the front of the eye. A probe called a pachymeter is gently placed on the front of the eye (the cornea) to measure its thickness. Pachymetry can help your diagnosis, because corneal thickness has the potential to influence eye pressure readings. With this measurement your Ophthamologist can better understand your eye pressures readings and develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Laser Procedures
Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) is a form of laser surgery that is used to lower intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients. It is used when eye drop medications are not lowering the eye pressure enough or are causing significant side effects. Laser energy is applied to the drainage tissue in the eye. This starts a chemical and biological change in the tissue that results in better drainage of fluid through the drain and out of the eye. This eventually results in lowering of Intraocular Pressure (IOP). It may take 1-3 months for the results to appear. The procedure takes only minutes and can be performed in the office.
YAG Laser Posterior Capsulotomy – The most common complication of cataract surgery is clouding of the part of the lens covering (capsule) that remains after surgery, called posterior capsule opacification (POC) – also referred to as “secondary cataract”. If the cloudiness affects your vision, you may choose to have a laser surgery called YAG posterior capsulotomy to correct this problem. They will use a laser to cut a hole in the clouded back lining of the lens capsule. This allows light to pass through the membrane to the retina at the back of the eye. The procedure takes only minutes and can be performed in the office.